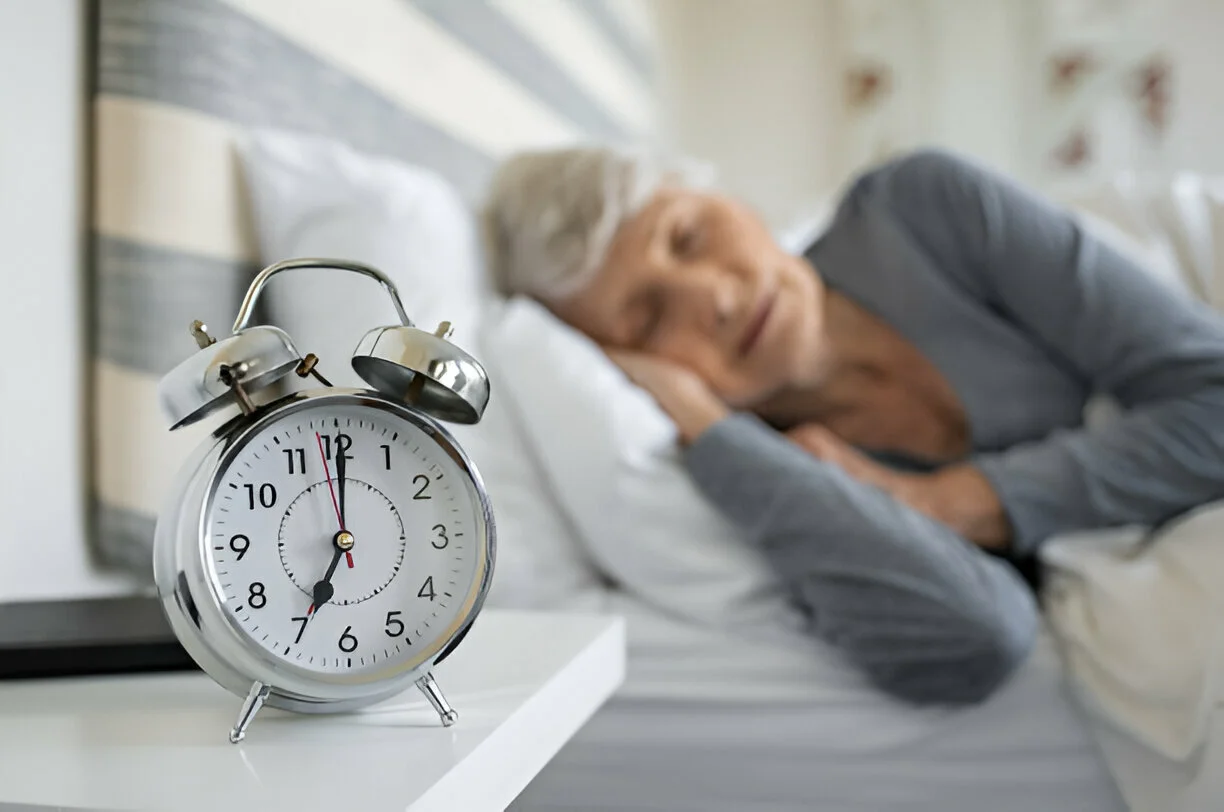
Sleep is a fundamental need for humans at all ages, including the elderly. Sleep needs that are well met can support physical and mental health, and improve overall quality of life. So, how long is the ideal sleep time for the elderly according to the World Health Organization (WHO)?
What is the Ideal Sleep Time for the Elderly?
According to WHO, elderly people aged 65 years and over need 7-9 hours of sleep per day. This duration is sufficient to maintain the health and function of the elderly body.
However, keep in mind that every individual's sleep needs are different. Factors such as health conditions, lifestyle, and medications taken can affect the sleep needs of the elderly.
- Signs that the elderly are getting enough sleep include:
- Feeling refreshed and energized after waking up
- Able to function well throughout the day
- Not feeling sleepy during the day
- Falling asleep easily and sleeping soundly
- Not waking up frequently during the night
If the elderly have difficulty sleeping or show signs of sleep deprivation, consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Benefits of Adequate Sleep for the Elderly
Adequate sleep provides many health benefits for the elderly, including:
- Improves cognitive function: Adequate sleep helps improve memory, concentration, and learning ability.
- Strengthens the immune system: Sleep helps the elderly body fight off infections and diseases.
- Maintains heart health: Adequate sleep helps lower the risk of high blood pressure, stroke and heart disease.
- Maintains mental health: Adequate sleep helps reduce the risk of depression, anxiety and mood swings.
- Improves quality of life: Getting enough sleep helps older adults feel more energetic, refreshed and happy.
Common Sleep Disorders Among the Elderly
Sleep is the key to opening the gates of health for the elderly. Unfortunately, this door is not always easy to walk through. Sleep disorders often lurk, disturbing peace and hampering energy recovery. Here are some “gatekeepers” that often interfere with the rest of the elderly.
1. Insomnia
Insomnia is like a ghost that haunts the nights of the elderly. Difficulty falling asleep, waking up repeatedly, and feeling inadequately rested after sleep characterize it. Imagine, feeling tired and lethargic during the day.
2. Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is like a monster that suffocates during sleep. Repeated pauses in breathing, loud snoring, gasping when awake, and headaches are signs of its presence. Not only daytime sleepiness, sleep apnea also increases the risk of serious illness.
3. Restless Leg Syndrome
Restless leg syndrome is like an unbearable tingle in the legs. This sensation usually occurs at night, when the elderly want to rest, making them keep moving their legs. The feeling of fatigue and sleepiness is inhibited.
4. Snoring
Snoring is like the sound of discordant music in the middle of the night. The vibration of the soft tissue in the throat when breathing produces a noise that disturbs the peace of sleep, both for the owner of the sound and the people around him. Snoring can also be a sign of sleep apnea.
5. Disrupted Circadian Rhythm
Circadian rhythms are like the body's internal clock that regulates the sleep-wake cycle. In the elderly, this clock can be disrupted, causing difficulty falling asleep or waking up in the morning. As a result, activity and mood are affected.
Impact of Sleep Deprivation on the Elderly
Sleep deprivation can have a negative impact on the health of the elderly, including:
- Fatigue and lack of energy
- Difficulty concentrating and remembering
- Decreased mood and depression
- Weakened immune system
- Increased risk of chronic diseases
- Accidents and injuries
Maintaining an ideal sleep schedule is very important for the health of older adults. With adequate and quality sleep, older adults can enjoy a healthier, happier and more productive life.